The Science of Moringa Tea Health Benefits

The Science Behind Moringa Tea and It’s Benefits
Commonly referred to as ‘horseradish or drumstick’ tree by locals, Moringa oleifera is consumed as a tea brewed from dried leaves, bark and seed. It’s nutritional and health benefits make it a popular drink in different parts of the world.The tree is a native to India but grows in Asia, Africa and South America.

Moringa leaves are rich in beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, and polyphenols which are natural antioxidants. Moringa’s healthful compounds also include vitamin A, B (thiamine), folate, calcium, potassium, iron, zinc, magnesium and phosphorus. Over the past few years scientists have studied the pharmacological functions and mechanisms of M. oleifera. Their research findings support the healthy benefits of adding Moringa tea to your daily wellness routine.
What are some of the benefits of Moringa tea?
1. Moringa has demonstrated anticancer properties. M. oleifera leaf and bark extracts have been shown to effectively inhibit the growth of breast, pancreatic, and colorectal cancer cells (1). Isothiocyanates have been described as potent anticancer compounds. These compounds occur naturally in M. oleifera. Moringa tea is a great source of polyphenol compounds such as flavonoids and phenolic acids.
2. In medical research Moringa leaf extract shows promise for supporting a healthy lipid blood profile (cholesterol) and reduce circulating blood glucose as a result of it’s phenolic acid compounds (2). In separate studies Moringa oleifera leaves consumed as tea and tinctures have demonstrated beneficial high-density lipoprotein and reduced low-density lipoproteins. More study is needed however drinking Moringa tea regularly may contribute to lower cholesterol numbers and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
3. Managing insulin resistance and maintaining healthy cholesterol numbers are two key components to healthy aging. In a 2018 study where subjects consumed a daily dose of Moringa in powder or tea, volunteers demonstrated improved glucose tolerance and decreased glucose uptake in response to slowed gastric emptying (4). Moringa has significantly decreased the incidence of hyperglycemia in multiple research studies.

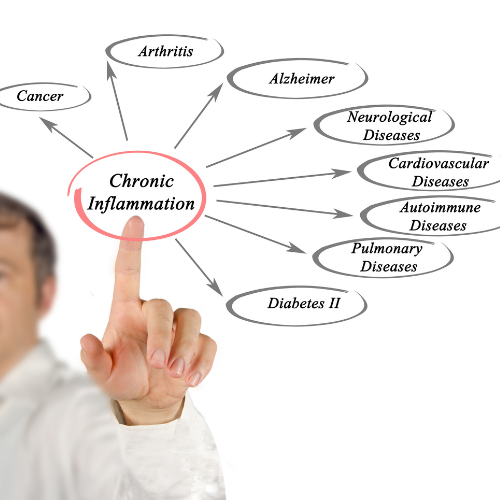
4. Moringa has a suppressive effect against chronic inflammation and it’s associated disorders primarily due to isoquercetin among other powerful phenolic compounds found in the leaves and bark. Inflammation is a normal response to stimuli in the body however chronic inflammation can lead to a range of serious health disorders such as high blood pressure, insulin resistance or diabetes, Crohn's, arthritis and cancer. The phenolic compounds produced by Moringa oleifera are well documented as possessing substantial anti-inflammatory properties.
5. The high levels of Vitamin C and other antioxidants stimulate the bodies production of white blood cells which help strengthen the immune system. Moringa tea is naturally caffeine free and is a natural energy booster which may support a healthy sleep/wake cycle improving circadian rhythms.
This adaptogenic nutrient packed superfood is widely used in Asian culinary recipes and ayurvedic remedies for stress relief, weight management, immunity strengthening and anti-inflammatory properties.
Download my free Moringa Tea Infographic Here

These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to diagnose treat cure or prevent any disease. This information is for educational purposes only and you are encouraged to seek the advice of your physician or naturopathic healthcare provider.
Sources:
1. Al-Asmari AK, Albalawi SM, Athar MT, Khan AQ, Al-Shahrani H, Islam M. Moringa oleifera as an Anti-Cancer Agent against Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0135814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135814. PMID: 26288313; PMCID: PMC4545797.
2. Wang F, Bao Y, Zhang C, Zhan L, Khan W, Siddiqua S, Ahmad S, Capanoglu E, Skalicka-Woźniak K, Zou L, Simal-Gandara J, Cao H, Weng Z, Shen X, Xiao J. Bioactive components and anti-diabetic properties of Moringa oleifera Lam. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(14):3873-3897. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1870099. Epub 2021 Jan 6. PMID: 33401950.
3. Mahajan SG, Mehta AA. Effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed extract on ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in guinea pigs. Inhal Toxicol. 2008 Aug;20(10):897-909. doi: 10.1080/08958370802027443. PMID: 18686107.
4. Ndong M, Uehara M, Katsumata S, Suzuki K. Effects of Oral Administration of Moringa oleifera Lam on Glucose Tolerance in Goto-Kakizaki and Wistar Rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2007 May;40(3):229-33. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.40.229. PMID: 18398501; PMCID: PMC2275769.


